ASP.NET MVC Model view controller ( MVC) Step by Step Part 1 ASP.NET MVC Model view controller ( MVC) Step by Step Part 2 ASP.NET MVC Model view controller ( MVC) Step by Step Part 3 ASP.NET MVC Model view controller ( MVC) Step by Step Part 4
Saturday, July 14, 2012
ASP.NET MVC Videos
ASP.NET MVC Model view controller ( MVC) Step by Step Part 1 ASP.NET MVC Model view controller ( MVC) Step by Step Part 2 ASP.NET MVC Model view controller ( MVC) Step by Step Part 3 ASP.NET MVC Model view controller ( MVC) Step by Step Part 4
ASP.Net MVC Sample Application
How to create a simple ASP.NET MVC program?
In this Exercise we will create a sample program using MVC template. So we will create a simple controller, attach the controller to simple index.aspx page and view the display on the browser.
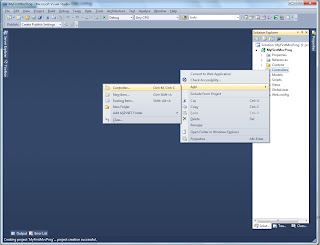
Step1:- Create project
Create a new project by selecting the MVC 2 empty web application template as shown in the below figure
After click ok button then we get structure with appropriate folders where we can add controllers, models and views.
Step 2:- Add controller
So let’s go and add a new controller as shown in the below figure.
Once you add the new controller you should see some kind of code snippet as shown in the below snippet.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.Mvc;
namespace MyFirstMvcProg.Controllers
{
public class Default1Controller : Controller
{
//
// GET: /Default1/
public ActionResult Index()
{
return View();
}
}
}
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.Mvc;
namespace MyFirstMvcProg.Controllers
{
public class Default1Controller : Controller
{
//
// GET: /Default1/
public ActionResult Index()
{
return View();
}
}
}
Step 3:- Add View
Now that we have the controller we need to go and add the view. So click on the Index function which is present in the control and click on add view menu as shown in the below figure.The add view pops up a modal box to enter view name which will be invoked when this controller is called as shown in the figure below. For now keep the view name same as the controller name and also uncheck the master page check box.Once you click on the ok button of the view, you should see a simple ASPX page with the below HTML code snippet. In the below HTML code snippet I have added “This is my first MVC application”.
Step 4:- Run the application
If you do a CNTRL + F5 You get error because we have not invoked the appropriate controller / action.If you append the proper controller on the URL you should be able to see the proper view.
Tuesday, June 12, 2012
WCF REST Service
REST stands for Representational State Transfer and is an architectural style. REST provides an easier way of data access comparing with the SOAP protocol. REST and SOAP relies on HTTP protocol.REST provides an alternative to SOAP and WSDL.
REST uses some common HTTP methods to insert/delete/update/retrieve information which is below:
JSON provides a simple alternative to the Fatty XML format of data representation. For example a class with properties name and age can be represented as:
eg:
{"Firstname" : "sudhakar",
"Lastname" : "Boyina",
"Address" : "Hyderabad"}
REST uses some common HTTP methods to insert/delete/update/retrieve information which is below:
- GET - Requests a specific representation of a resource
- PUT - Creates or updates a resource with the supplied representation
- DELETE - Deletes the specified resource
- POST - Submits data to be processed by the identified resource
What is JSON?
JSON represents JavaScript Object Notation and is an open standard lightweight data interchange format in human readable form. Shortly, it is a data representation format.JSON provides a simple alternative to the Fatty XML format of data representation. For example a class with properties name and age can be represented as:
eg:
{"Firstname" : "sudhakar",
"Lastname" : "Boyina",
"Address" : "Hyderabad"}
Search result 2
Search result 3
Sunday, June 10, 2012
wcf Interview Questions and Answers
|
|
|
|
|
What is WCF?
Windows Communication Foundation (WCF) is an SDK for developing and deploying services on Windows. WCF provides a runtime environment for services, enabling you to expose CLR types as services, and to consume other services as CLR types. WCF is part of .NET 3.0 and requires .NET 2.0, so it can only run on systems that support it.
Difference between WCF and Web
services?
1.Web Services can be accessed only over HTTP
2.Web Services works in stateless environment WCF is flexible because its services can be hosted in different types of applications. The following lists several common scenarios for hosting WCF services: 1. IIS 2. WAS 3. Self-hosting 4. Managed Windows Service |
|
|
What are the various ways of
hosting a WCF service?
Self hosting the service in his own application domain. This we have already covered in the first section. The service comes in to existence when you create the object of ServiceHost class and the service closes when you call the Close of the ServiceHost class. Host in application domain or process provided by IIS Server. Host in Application domain and process provided by WAS (Windows Activation Service) Server. |
|
|
What are three major points in
WCF?
We Should remember ABC. Address - Specifies the location of the service which will be like http://Myserver/MyService.Clients will use this location to communicate with our service. Binding - Specifies how the two paries will communicate in term of transport and encoding and protocols. Contract - Specifies the interface between client and the server.It's a simple interface with some attribute. |
|
|
What was the code name for WCF?
The code name of WCF was Indigo . WCF is a unification of .NET framework communication technologies which unites the following technologies:- NET remoting MSMQ Web services COM+ |
|
|
What are the main components of
WCF?
The main components of WCF are 1. Service class 2. Hosting environment 3. End point |
|
|
What are different elements of WCF
Srevices Client configuration file?
WCF Services client configuration file contains endpoint, address, binding and contract. A sample client config file looks like |
|
|
What is Proxy and how to generate
proxy for WCF Services?
WCF Services client configuration file contains endpoint, address, binding and contract. A sample client config file looks like The proxy is a CLR class that exposes a single CLR interface representing the service contract. The proxy provides the same operations as service's contract, but also has additional methods for managing the proxy life cycle and the connection to the service. The proxy completely encapsulates every aspect of the service: its location, its implementation technology and runtime platform, and the communication transport. The proxy can be generated using Visual Studio by right clicking Reference and clicking on Add Service Reference. This brings up the Add Service Reference dialog box, where you need to supply the base address of the service (or a base address and a MEX URI) and the namespace to contain the proxy. Proxy can also be generated by using SvcUtil.exe command-line utility. We need to provide SvcUtil with the HTTP-GET address or the metadata exchange endpoint address and, optionally, with a proxy filename. The default proxy filename is output.cs but you can also use the /out switch to indicate a different name. SvcUtil http://localhost/MyService/MyService.svc /out:Proxy.cs When we are hosting in IIS and selecting a port other than port 80 (such as port 88), we must provide that port number as part of the base address: SvcUtil http://localhost:88/MyService/MyService.svc /out:Proxy.cs |
|
|
What are contracts in WCF?
In WCF, all services expose contracts. The contract is a platform-neutral and standard way of describing what the service does. WCF defines four types of contracts. Service contracts Describe which operations the client can perform on the service. There are two types of Service Contracts. ServiceContract - This attribute is used to define the Interface. OperationContract - This attribute is used to define the method inside Interface. [ServiceContract] interface IMyContract { [OperationContract] string MyMethod( ); } class MyService : IMyContract { public string MyMethod( ) { return "Hello World"; } } Data contracts Define which data types are passed to and from the service. WCF defines implicit contracts for built-in types such as int and string, but we can easily define explicit opt-in data contracts for custom types. There are two types of Data Contracts. DataContract - attribute used to define the class DataMember - attribute used to define the properties. [DataContract] class Contact { [DataMember] public string FirstName; [DataMember] public string LastName; } If DataMember attributes are not specified for a properties in the class, that property can't be passed to-from web service. Fault contracts Define which errors are raised by the service, and how the service handles and propagates errors to its clients. Message contracts Allow the service to interact directly with messages. Message contracts can be typed or untyped, and are useful in interoperability cases and when there is an existing message format we have to comply with. |
|
|
What is the address formats of the
WCF transport schemas?
Address format of WCF transport schema always follow [transport]://[machine or domain][:optional port] format. for example: HTTP Address Format http://localhost:8888 the way to read the above url is "Using HTTP, go to the machine called localhost, where on port 8888 someone is waiting" When the port number is not specified, the default port is 80. TCP Address Format net.tcp://localhost:8888/MyService When a port number is not specified, the default port is 808: net.tcp://localhost/MyService NOTE: Two HTTP and TCP addresses from the same host can share a port, even on the same machine. IPC Address Format net.pipe://localhost/MyPipe We can only open a named pipe once per machine, and therefore it is not possible for two named pipe addresses to share a pipe name on the same machine. MSMQ Address Format net.msmq://localhost/private/MyService net.msmq://localhost/MyService |
|
|
What is endpoint in WCF?
Every service must have Address that defines where the service resides, Contract that defines what the service does and a Binding that defines how to communicate with the service. In WCF the relationship between Address, Contract and Binding is called Endpoint. The Endpoint is the fusion of Address, Contract and Binding. |
|
|
What is binding and how many types
of bindings are there in WCF?
A binding defines how an endpoint communicates to the world. A binding defines the transport (such as HTTP or TCP) and the encoding being used (such as text or binary). A binding can contain binding elements that specify details like the security mechanisms used to secure messages, or the message pattern used by an endpoint. WCF supports nine types of bindings. Basic binding Offered by the BasicHttpBinding class, this is designed to expose a WCF service as a legacy ASMX web service, so that old clients can work with new services. When used by the client, this binding enables new WCF clients to work with old ASMX services. TCP binding Offered by the NetTcpBinding class, this uses TCP for cross-machine communication on the intranet. It supports a variety of features, including reliability, transactions, and security, and is optimized for WCF-to-WCF communication. As a result, it requires both the client and the service to use WCF. Peer network binding Offered by the NetPeerTcpBinding class, this uses peer networking as a transport. The peer network-enabled client and services all subscribe to the same grid and broadcast messages to it. IPC binding Offered by the NetNamedPipeBinding class, this uses named pipes as a transport for same-machine communication. It is the most secure binding since it cannot accept calls from outside the machine and it supports a variety of features similar to the TCP binding. Web Service (WS) binding Offered by the WSHttpBinding class, this uses HTTP or HTTPS for transport, and is designed to offer a variety of features such as reliability, transactions, and security over the Internet. Federated WS binding Offered by the WSFederationHttpBinding class, this is a specialization of the WS binding, offering support for federated security. Duplex WS binding Offered by the WSDualHttpBinding class, this is similar to the WS binding except it also supports bidirectional communication from the service to the client. MSMQ binding Offered by the NetMsmqBinding class, this uses MSMQ for transport and is designed to offer support for disconnected queued calls. MSMQ integration binding Offered by the MsmqIntegrationBinding class, this converts WCF messages to and from MSMQ messages, and is designed to interoperate with legacy MSMQ clients. |
|
|
Where we can host WCF services?
Every WCF services must be hosted somewhere. There are three ways of hosting WCF services. They are 1. IISM 2. Self Hosting 3. WAS (Windows Activation Service) |
|
|
What is address in WCF and how
many types of transport schemas are there in WCF?
Address is a way of letting client know that where a service is located. In WCF, every service is associated with a unique address. This contains the location of the service and transport schemas. WCF supports following transport schemas HTTP TCP Peer network IPC (Inter-Process Communication over named pipes) MSMQ The sample address for above transport schema may look like http://localhost:81 http://localhost:81/MyService net.tcp://localhost:82/MyService net.pipe://localhost/MyPipeService net.msmq://localhost/private/MyMsMqService net.msmq://localhost/MyMsMqService |
|
|
What is service and client in
perspective of data communication?
A service is a unit of functionality exposed to the world. The client of a service is merely the party consuming the service |
Difference between WCF and Web service
Web Service in ASP.NET
A Web Service is programmable application logic accessible via standard Web protocols. One of these Web protocols is the Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP). SOAP is a W3C submitted note (as of May 2000) that uses standards based technologies (XML for data description and HTTP for transport) to encode and transmit application data.Consumers of a Web Service do not need to know anything about the platform, object model, or programming language used to implement the service; they only need to understand how to send and receive SOAP messages (HTTP and XML).
WCF Service
Windows Communication Foundation (WCF) is a framework for building service-oriented applications. Using WCF, you can send data as asynchronous messages from one service endpoint to another. A service endpoint can be part of a continuously available service hosted by IIS, or it can be a service hosted in an application. An endpoint can be a client of a service that requests data from a service endpoint. The messages can be as simple as a single character or word sent as XML, or as complex as a stream of binary data.In what scenarios must WCF be used
- A secure service to process business transactions.
- A service that supplies current data to others, such as a traffic report or other monitoring service.
- A chat service that allows two people to communicate or exchange data in real time.
- A dashboard application that polls one or more services for data and presents it in a logical presentation.
- Exposing a workflow implemented using Windows Workflow Foundation as a WCF service.
- A Silverlight application to poll a service for the latest data feeds.
Features of WCF
- Service Orientation
- Interoperability
- Multiple Message Patterns
- Service Metadata
- Data Contracts
- Security
- Multiple Transports and Encodings
- Reliable and Queued Messages
- Durable Messages
- Transactions
- AJAX and REST Support
- Extensibility
Difference between Web Service in ASP.NET & WCF Service
Web service is a part of WCF. WCF offers much more flexibility and portability to develop a service when comparing to web service. Still we are having more advantages over Web service, following table provides detailed difference between them.| Features | Web Service | WCF |
|---|---|---|
| Hosting | It can be hosted in IIS | It can be hosted in IIS, windows activation service, Self-hosting, Windows service |
| Programming | [WebService] attribute has to be added to the class | [ServiceContraact] attribute has to be added to the class |
| Model | [WebMethod] attribute represents the method exposed to client | [OperationContract] attribute represents the method exposed to client |
| Operation | One-way, Request- Response are the different operations supported in web service | One-Way, Request-Response, Duplex are different type of operations supported in WCF |
| XML | System.Xml.serialization name space is used for serialization | System.Runtime.Serialization namespace is used for serialization |
| Encoding | XML 1.0, MTOM(Message Transmission Optimization Mechanism), DIME, Custom | XML 1.0, MTOM, Binary, Custom |
| Transports | Can be accessed through HTTP, TCP, Custom | Can be accessed through HTTP, TCP, Named pipes, MSMQ,P2P, Custom |
| Protocols | Security | Security, Reliable messaging, Transactions |
BOOKS
VC1 | English | 704x528 | WMV | 2 fps 1045 kbps | 44100 Hz 96 kbps | 657 MB
Genre: eLearning
Microsoft's 5 part firestarter for WCF
Part 1: Keynote Intro to SOA & WCF
Part 2: Most Common WCF Usage Configurations
Part 3: REST Programming with WCF
Part 4: WCF Made Easy Data & RIA Services
Part 5: What's New with WCF 4.0
Genre: eLearning
Microsoft's 5 part firestarter for WCF
Part 1: Keynote Intro to SOA & WCF
Part 2: Most Common WCF Usage Configurations
Part 3: REST Programming with WCF
Part 4: WCF Made Easy Data & RIA Services
Part 5: What's New with WCF 4.0
Windows Communication Foundation For Beginners warez index
Programming WCF Services, 2nd Edition

Programming WCF Services will teach you how to design and develop SOA-WCF-based applications. You will need to be an experienced developer who has a fair understanding of .NET and C# 2.0. A couple of points about Programming WCF Services, first, this isn't a beginners book; the author dives down into advanced material in spots almost without notice. If you want to become proficient using WCF, you will be buying this book eventually. You will find that this book will become both a reference as well as well as a guide.
Author : Juval Lowy
ISBN : 978-0-596-52130-1
Wrox-Professional WCF Programming

Author : Scott Klein
ISBN : 9780470089842
Microsoft Windows Communication Foundation Step by Step

Author : John Sharp
ISBN : 9780735623361
Pro WCF: Practical Microsoft SOA Implementation Book Description

Author : Chris Peiris, Dennis Mulder, Shawn Cicoria,
ISBN : 1590597028
Microsoft Windows Communication Foundation: Hands-on

Author : Craig McMurtry
ISBN : 0672328771
Learning WCF

Author : Michele Leroux Bustamante
ISBN : 978-0-596-10162-6
Windows Communication Foundation 3.5 Unleashed Book
Publisher: S.a.m.s 2008 | 768 Pages | ISBN: 0672330245 | PDF | 14 MB
Windows Communication Foundation (WCF) is Microsoft’s dynamic technology for allowing autonomous software to communicate. Superseding earlier technologies such as COM/DCOM, .NET Remoting, ASP.NET Web Services, and the Web Services Enhancements for .NET, WCF provides a single solution that is designed to always be the best way to exchange data among software entities. It also provides the infrastructure for developing the next generation of Web Services, with support for the WS-* family of specifications, and a new serialization system for enhanced performance. In the 3.5 release, WCF has been expanded to include support for REST, JSON, and Syndication (RSS and Atom) services, further broadening the possibilities for what can be done. For information technology professionals, WCF supplies an impressive array of administration tools that enterprises and software vendors can use to reduce the cost of ownership of their solutions without writing a single line of code. Most important, WCF delivers on the promise of model-driven software development with the new software factory approach, by which one can iteratively design solutions in a modeling language and generate
executables from lower-level class libraries.
Saturday, June 9, 2012
WCF Indroduction
WINDOWS COMMUNICATION FOUNDATION
Overview
Windows Communication Foundation takes many existing
communication technologies, such as Web Services, Windows Remoting, Microsoft
Message Queuing, and abstracts them into a single technology. In most cases, this simplifies the way you
communicate with other applications. It
also allows you to communicate with other applications without being coupled to
a specific technology. Therefore, you
could use Web Services over SOAP to begin with, and later move to remote
procedure calls (RPC) without changing your code, just the configuration of
WCF.
The Basics
There are a
few basic tasks when creating a WCF service.
The basic tasks that must be performed are, in order:
- Define the service contract. A service contract specifies the signature of a service, the data it exchanges, and other contractually required data.
- Implement the contract. To implement a service contract, create the class that implements the contract and specify some custom behaviors that the runtime should have.
- Configure the service by specifying endpoint information and other behavior information.
- Host the service in an application.
- Build a client application.
For more
information, see http://msdn2.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms732098.aspx
Example
To display a
step-by-step enactment of the above steps, let’s define a web service that
reports the current date/time:
1.1 Define a Service Contract
First, let’s create a project to house our service
contract. Let’s call it WCFDateTime.Service.
1.2 Define a Service Contract
Then, let’s define an interface that represents the service
we’re going to provide. In this case,
let’s call it IDateTimeService.
public interface IDateTimeService
{
}
1.3 Define a Service Contract
We need to add a method to our service
that will return the current date/time:
public interface IDateTimeService
{
DateTime
GetCurrentDateTime();
}
1.4 Define a Service Contract
Now, we need to decorate our code with attributes so that WCF
will recognize our interface and its methods.
Namely, we will add the following attributes:
·
ServiceContractAttribute
o
Identifies an interface as a WCF service
contract
·
OperationContractAttribute
o
Identifies methods of an interface as WCF
service operations, that is, methods that can be called through WCF
using System.ServiceModel;
[ServiceContract]
public interface IDateTimeService
{
[OperationContract]
DateTime
GetCurrentDateTime();
}
In order to use the above attributes,
you’ll need to add a reference to the System.ServiceModel assembly. The service contract is now ready to be used.
2.1 Implement the Contract
Now
that we’ve defined our service contract, we can move on to implementing
it. First, let’s create another project
to house our server application. Let’s
call it WCFDateTime.Server, and make it a Console Application
project.
2.2 Implement the Contract
Now,
let’s implement the IDateTimeService. The implementation
is going to run on our server, to provide the date/time to whoever is going to
consume our service.
In
the WCFDateTime.Server project, let’s create a class called
DateTimeService and have it implement IDateTimeService:
using WCFDateTime.Service;
public class DateTimeService :
IDateTimeService
{
}
Remember to add a reference to the WCFDateTime.Service
project so you can use IDateTimeService.
2.3 Implement the Contract
The
above code will obviously not compile, because we did not implement the GetCurrentDateTime method:
public class DateTimeService :
IDateTimeService
{
public
DateTime GetCurrentDateTime()
{
return
DateTime.Now;
}
}
That’s it! The DateTimeService is now ready to be used.
3.1 Configure the Service
Now we need to configure our service so it can be consumed by
client applications. The simplest way to
accomplish this is by adding an application configuration file (app.config or
web.config) to the WCFDateTime.Server project:
<?xml version="1.0"
encoding="utf-8" ?>
<configuration>
<system.serviceModel>
<services>
<service name="WCFDateTime.Server.DateTimeService">
<endpoint
address="http://localhost:8081/DateTimeService"
binding="wsHttpBinding"
contract="WCFDateTime.Service.IDateTimeService" />
</service>
</services>
</system.serviceModel>
</configuration>
When defining an endpoint for WCF,
remember your A-B-Cs:
1.
Address (where)
2.
Binding (how)
3.
Contract (what)
The address specifies the address where you
want the service to be located.
The binding specifies the transport you want to
use in order to provide the service.
The contract specifies what service will be
provided
4.1 Host the Service in an Application
Now that WCF has been configured, the simplest way to host
this service is to create a Console Application and use the ServiceHost class. First, add a reference to the System.ServiceModel assembly. Then, In the program.cs file of WCFDateTime.Server, do the following:
using System.ServiceModel;
namespace WCFDateTime.Server
{
class Program
{
static public void Main(string[] args)
{
// Get a host for our service
ServiceHost serviceHost = new
ServiceHost(
typeof(DateTimeService)
);
// Open the service host to start
listening for incoming requests
serviceHost.Open();
// The service can now be accessed
Console.WriteLine("The service is ready.");
Console.WriteLine("Press <ENTER> to terminate
service.");
Console.ReadLine();
// Close the service host
serviceHost.Close();
}
}
}
By simply running this application, we expose our service so
that client applications can use it.
5.1 Build a Client Application
To build a client application, we must create a new project
for it. Let’s call it WCFDateTime.Client, and make it a Console Application
as well.
5.2 Build a Client Application
Now, we need to add an Application Configuration file, and
give it some settings that will allow us to connect to the service we just
created:
<?xml version="1.0"
encoding="utf-8"?>
<configuration>
<system.serviceModel>
<client>
<endpoint
address="http://localhost:8081/DateTimeService"
binding="wsHttpBinding"
contract="WCFDateTime.Service.IDateTimeService"
name="MyDateTimeService">
</endpoint>
</client>
</system.serviceModel>
</configuration>
Now that our we’ve configured our WCF client, we can connect
to it. There are two ways to connect to
the WCF service we previously created:
1.
Client proxy generation
2.
Channel
factories
Most Microsoft articles will point you in the direction of
using client proxies; however, for our purposes, channel factories
are quicker to implement and more robust in a Model/View/Presenter
architecture.
5.3 Build a Client Application
Now, add a reference to the System.ServiceModel and WCFDateTime.Service assemblies,
and then add the following to the program.cs file:
using System.ServiceModel;
using WCFDateTime.Service;
class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Get a channel factory for our
service,
// using the configuration for
"MyDateTimeService"
// in the application configuration
file.
ChannelFactory<IDateTimeService>
channelFactory =
new
ChannelFactory<IDateTimeService>("MyDateTimeService");
// Get an instance of our service
IDateTimeService service =
channelFactory.CreateChannel();
// Get the server’s date/time
DateTime dt = service.GetCurrentDateTime();
// Write the current server date/time
Console.WriteLine("The current
server time is " + dt);
// Close the connection to our service
channelFactory.Close();
}
}
5.4 Build a Client Application
Your client application is now ready to run! Simply start the WCFDateTime.Server application, and once it’s running,
run the WCFDateTime.Client application to see it work!
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)